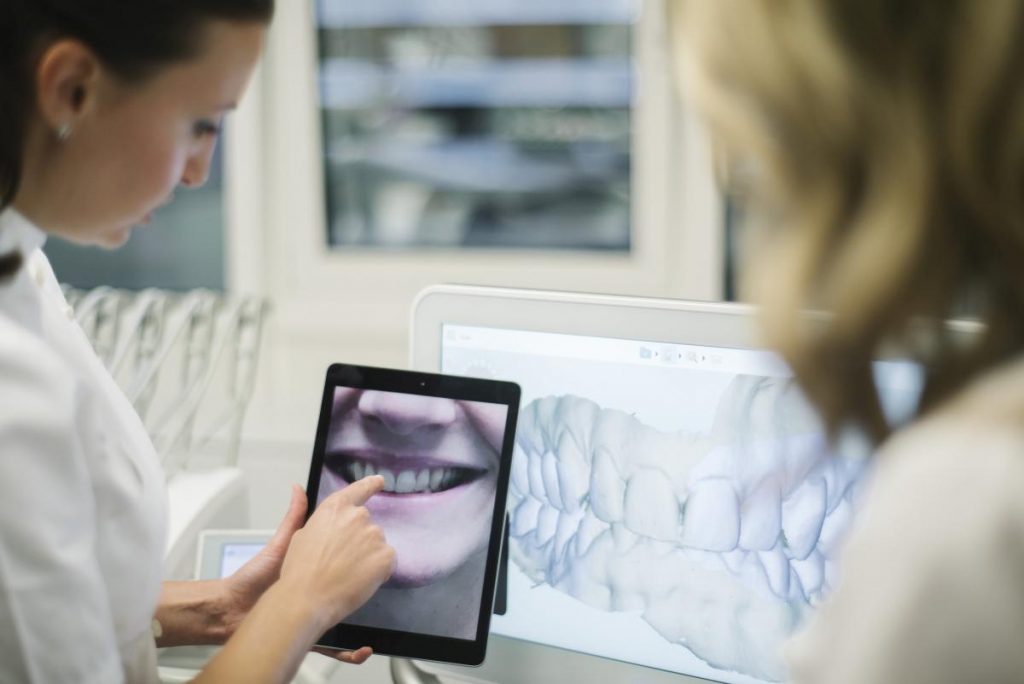
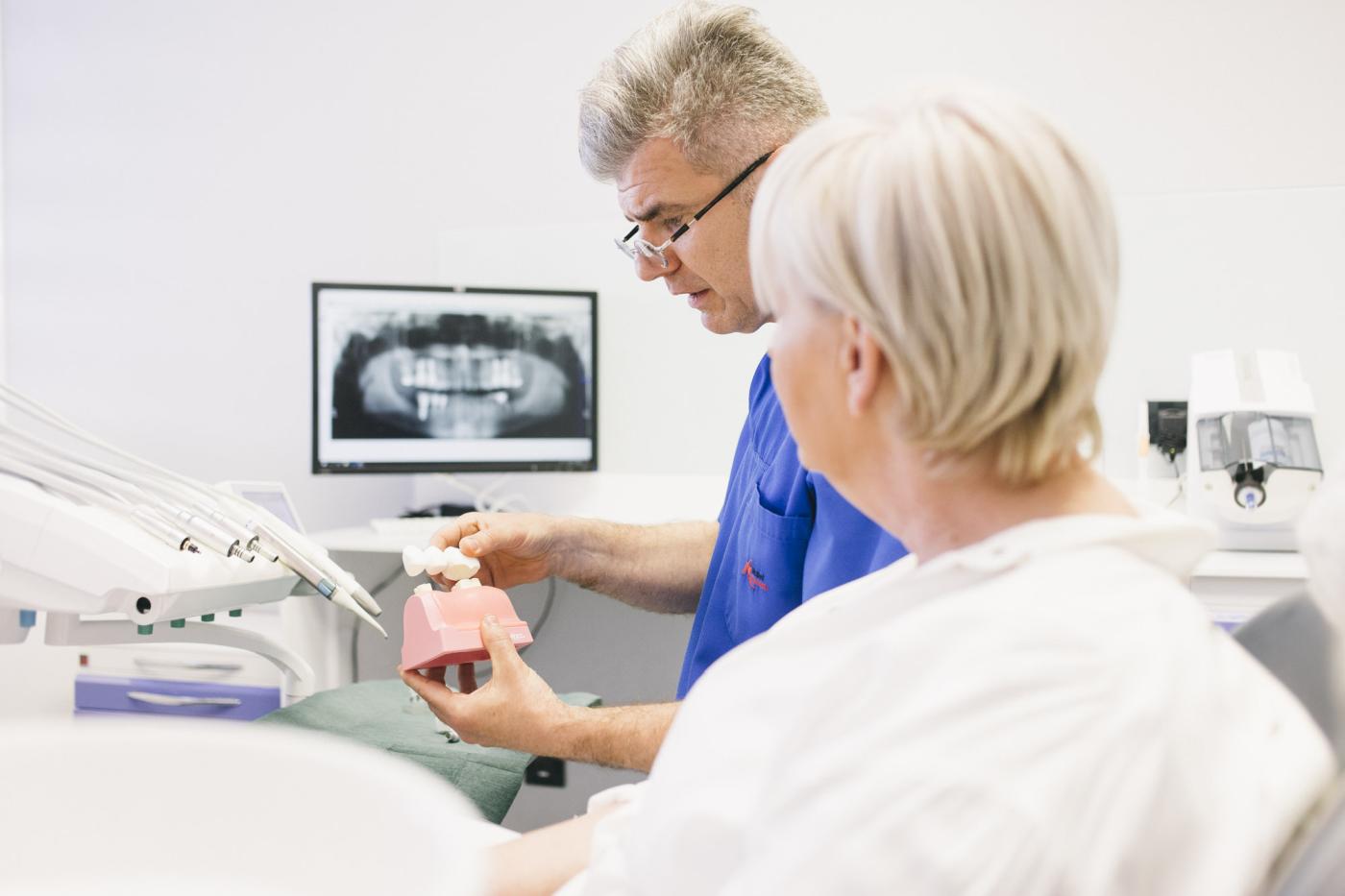
What is periodontitis?
The most common cause of gingivitis, gum bleeding or tooth mobility is periodontitis, or the so-called gum disease. It is often considered to be an incurable disease affecting the elderly population. Periodontitis is a disease caused by bacteria and can occur for several reasons. It has a genetic background, and it is aided by various local factors in the oral cavity, such as tooth crowding or poor prosthetic work, dated fillings and so on. Also, some systemic diseases and conditions like smoking or diabetes are a favourable circumstance for periodontitis. Periodontitis begins with bleeding and pain in the gum area and develops by forming inflammatory pockets along with the pulling of the gums and bones around the teeth. Finally, it affects the mobility of one, few or all teeth. The terminal stage is characterized by tooth decay, the change of position and the tooth-loss in the end.
Periodontology in Dental Polyclinic Jelusic
Periodontitis has serious effects on general health
Interestingly, periodontitis affects the clinical picture of diabetes. The existence of an interaction between the treatment of such diseases has been proven – the treatment of periodontitis improves BS conditions, while controlled diabetes enhances the treatment of periodontal disease. Untreated periodontitis increases the possibility of a stroke and a heart attack along with influencing premature childbirth in pregnant women.
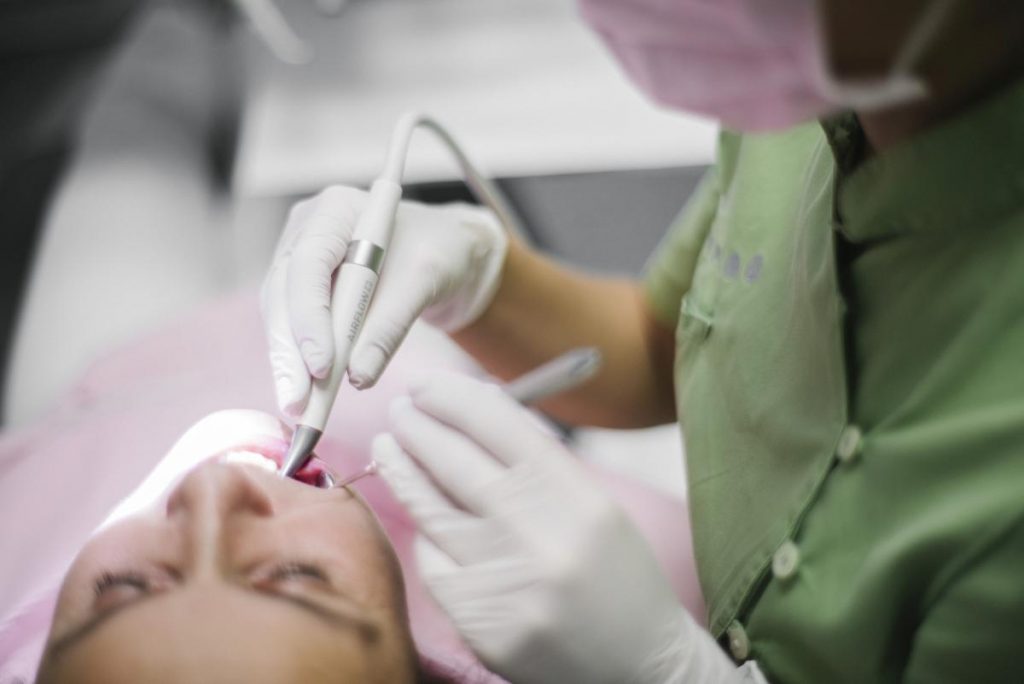
Periodontitis can be treated and cured
It is a condition that must not be ignored, and it requires professional treatment. Periodontitis is a disease caused by specific periodontal bacteria. It can be local or generalized, a.k.a. chronic or aggressive. It can affect all age groups, not just the elderly population. When it comes to younger people, its effects are usually more aggressive. Periodontitis requires an accurate diagnosis and special periodontist treatment, but also a routine follow-up and regular monitoring. During every check-up, it is necessary to re-evaluate the condition of the tooth’s supporting tissue (the gums around the tooth) and adjust the methods of treatment and maintenance to the patient’s specific situation.
Non-surgical and surgical therapy
When it comes to the periodontal therapy execution, it is important to use modern diagnostic technologies in order to correctly determine and monitor therapy results. Likewise, the clinician should use a variety of surgical and non-surgical therapies. Speaking from a therapeutical point of view, we have at our disposal various conventional non-surgical therapies (manual, machine, ultrasound, photodynamic, laser), as well as surgical therapy. Surgical therapy can also include advanced guided tissue regeneration techniques or classical techniques aimed at removing and “cleaning pockets” as well as establishing harmony of the teeth’s supporting structures, which will ensure a favourable and long-term perspective of the situation.
The therapy’s integrity – a multidisciplinary approach
When working with periodontal-compromised patients, overall consideration of the therapy is extremely important. In fact, such patients are virtually always in need not only for gum treatment, but also for prosthetic work which would make up for one, a few or all teeth. When creating classic bridges and crowns, it is important to cure the gums before the prosthetic phase, in order to prognostically assess the stability of the tooth and the possibility of its potential future periodontal supply.
In any case, periodontally compromised patients along with gingivitis patients should be exposed to periodontological rehabilitation before any prosthetic therapy. Healthy gums are the key to any successful and long-lasting prosthetic procedure!